Is Liver Pain in Back Common? The Connection Between The Two
 Written By
Jaclyn P. Leyson-Azuela, RMT, MD, MPH
Written By
Jaclyn P. Leyson-Azuela, RMT, MD, MPH
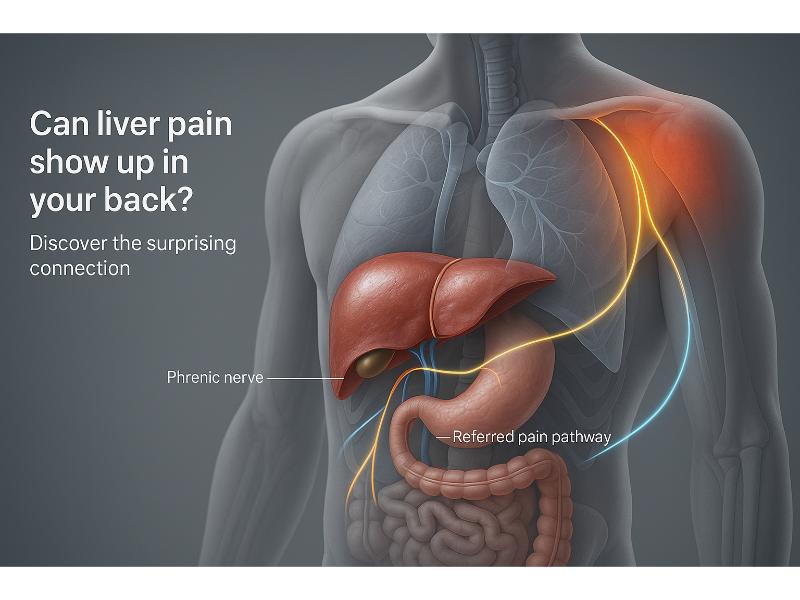
The human body is a complex vessel and sometimes pain can be in one area even when it affects another. The intricate connections of the nerves made this possible. When the discomfort strikes the back, it’s normal to consider causes inherent to it like muscle strain or poor posture. But what if liver pain in back is the cause of it? Is it possible to have this effect? The liver is often an overlooked organ in the context of back pain.
Here’s what you need to know about the connection between the two. In this article, we will tackle the signs, causes, and when to seek medical guidance.
Key Insights
-
Liver problems can cause back pain, especially in the upper right back or shoulder
-
Pain that is coming from another part of the body and is manifested elsewhere is called referred pain
-
Common causes of referred pain include liver cancer, cirrhosis, hepatitis, and fatty liver disease
-
Symptoms include abdominal pain, jaundice, tiredness you haven’t experienced before, swelling, dark urine, and itchy skin
-
See a doctor if you experience persistent pain with liver symptoms
-
Seek immediate medical care if there is confusion or coma
-
Diagnosis involves blood tests, imaging, and physical exams
-
Treatment varies by cause, including medications, lifestyle changes, or surgery
-
Prevention includes healthy lifestyle changes, limit alcohol intake, and getting vaccinations for hepatitis
Can Liver Problems Cause Back Pain?
Yes, liver problems can cause back pain.
About 10% of the population in the United States have some form of liver disease. This highlights how common and widespread liver disease is and it is crucial to consider it when you’re experiencing unexplained discomfort. It may be surprising but liver problems can indeed cause back pain.
What is Liver Pain in the Back?
When you experience liver pain in the back, it’s natural to ask why and what causes it. It is often a result of referred pain. This is the pain that originates from the liver but can be felt over the shoulder or upper right back.
The liver is located in the upper right part of the abdomen. It can cause pain to radiate to your back because of the shared nerve pathways. This natural phenomenon makes it tricky to pinpoint the exact origin of the pain since the pain may not be over the liver itself.
This concept is a basic foundation for understanding back pain and where it really originates, particularly if it cannot be explained by any musculoskeletal issues. The pain can be a dull ache or a more sharp, localized sensation, depending on the underlying condition. It’s also important to differentiate between this and the common back pain. The liver-related back pain may be associated with other symptoms.
How do liver problems cause back pain?
The liver can cause back pain through several mechanisms, including:
-
Inflammation that irritates the surrounding tissues
-
Enlargement that presses on the nerves
-
Tumors that causes pressure
When livers are inflamed, in conditions like hepatitis, it can swell and stretch its covering called capsule, which is rich in nerve endings. The stretching can lead to pain that is not only localized to the abdomen but also can be referred to the back.
Additionally, if the liver enlarges significantly, it can press on nearby organs, muscles, or nerves. It leads to discomfort that is felt in the back as it radiates.
In more serious cases like liver cancer, tumors can grow and exert direct pressure on adjacent structures, including the diaphragm or nerves that share the same pathway as the back. This could result in persistent or sometimes sharp, severe back pain.
It’s a complex interplay of physical pressure and nerve irritation that translates liver issues into the back for it to cause discomfort. These mechanisms help clarify why the problem in your liver may manifest as pain, which is far from the organ itself.
What Are Common Liver Conditions That Cause Back Pain?

Several liver conditions may lead to back pain. Each of these will have its own specific way of affecting the body. These conditions could range from inflammatory diseases to more serious illnesses like cancer.
Here are some common liver conditions that can manifest as back pain:
-
Liver cancer
This is a serious condition where the malignant cells develop in the liver. When the tumor grows, it can press on surrounding tissues and nerves, which could be felt on the back or shoulder as pain or discomfort. The pain often indicates that the malignancy has advanced to a later stage.
-
Hepatitis
This is the inflammation of the liver, often caused by viral infections (e.g., hepatitis A, B, or C), alcohol, or autoimmune diseases.
-
Cirrhosis
A late-stage condition from liver scarring or fibrosis, which is caused by different causes of liver diseases or conditions like hepatitis and chronic alcoholism. As the liver is filled with scarring, it hardens and shrinks, which could result in portal hypertension and ascites (buildup of fluid in the abdomen). The latter complications can cause pressure and referred pain to the back.
-
Fatty liver disease (FLD)
This refers to the accumulation of fat on the liver cells. The condition is often silent in the early stage but non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which is a more severe form of FLD, can cause inflammation and liver damage. As a result, it may manifest as dull ache or fullness but may sometimes be felt at the back. About 30% of Americans have FLD, which is a silent but progressing disease.
Each of these conditions can affect the liver in different mechanisms. But the common thread is that they have the potential to cause referred pain in the back.
What is Liver Cancer and How Does It Cause Back Pain?

Liver cancer can cause back pain as the tumor grows large enough to exert pressure on nearby organs or nerves, or when the cancer spreads to the spine.
The pain is often a sign that the liver cancer has advanced since early-stage disease doesn’t typically cause noticeable symptoms. The discomfort or pain may be persistently achy and it can worsen over time.
Nonetheless, you need to be aware that while back pain may be a symptom, it is usually associated with other liver-specific symptoms of dysfunction, such as:
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
Extreme fatigue not relieved by rest
-
Jaundice
Statistics show that survival rates for liver cancer is more than 50%, particularly when it is detected early and can be removed safely. Therefore, it is important to recognize potential symptoms that may pertain to liver cancer or other liver-related dysfunction and seek timely medical care.
Can Hepatitis Lead to Back Pain?
Yes, hepatitis can lead to back pain because of the inflammation it brings to the liver. The liver swells and thus places pressure on the surrounding tissues and nerves.
Hepatitis is caused by various viruses including hepatitis A, B, or C. It can also be caused by other factors that directly affect the liver’s health. The inflammation can make the liver larger, which may result in a dull, aching sensation that can radiate to the back or shoulder.
However, you need to remember that back pain will not always be present with hepatitis but it can be a significant symptom for other individuals. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) states that millions of Americans have viral hepatitis but many are unaware of their condition. So it is important to recognize all potential symptoms, including referred pain.
Does Cirrhosis Cause Back Pain?
Yes, cirrhosis can cause back pain through referred pain. It is a severe scarring of the liver, which makes the liver enlarge or make you develop ascites.
When liver tissues are replaced by scarring, the liver struggles to perform its functions such as metabolizing nutrients. Studies have demonstrated that about 13.92% of patients with liver cirrhosis experience low back pain and it is often related to the chronic inflammatory state and structural changes that occur within the liver.
As previously noted, the back pain is often accompanied by symptoms related to cirrhosis, such as:
-
Jaundice
-
Fatigue
-
Swelling in the legs
Is Back Pain a Symptom of Fatty Liver Disease?
FLD does not present symptoms during early stages but it commonly presents as dull ache or fullness on the upper right abdomen as it progresses. The advanced stage, specifically the NASH, can present inflammatory and liver dysfunction symptoms.
When you experience persistent back pain and is often related to unexplained weight gain and fatigue, it is important to consider FLD.
What Symptoms Are Associated and Liver-Related Back Pain?

When back pain comes from the liver, it often comes with other related symptoms that will help differentiate it from the common musculoskeletal back pain. These related signs are crucial indicators that indicate the liver may be struggling. Recognizing these additional symptoms is essential to understand the true source of the discomfort and seeking appropriate medical attention.
Here are common symptoms that may accompany liver-related back pain:
-
Abdominal pain (particularly in the upper right abdominal area)
-
Fatigue
-
Leg swelling (edema particularly in the ankles and legs)
-
Dark urine
-
Pale stools
-
Itchy skin (pruritus)
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Loss of appetite
-
Weight loss
These symptoms, when present alongside back pain, are red flags and should prompt a visit to a healthcare facility. Unlike typical back pain that may respond to rest, physical therapy, or over-the-counter (OTC) pain meds, liver-related back pain often requires treatment and management of the underlying medical condition before it resolves.
When Should You See a Doctor for Liver Pain in the Back?
It’s crucial to seek medical attention if you experience persistent back pain particularly when accompanied by symptoms that suggest liver involvement. Not all back pain is serious, but there are certain signs that warrant immediate medical assessment to rule out or manage liver issues.
Here are some guidelines on when you should seek medical consult:
-
Persistent back pain with liver symptoms
-
Sudden, severe back pain
-
Changes in mental state
-
History of liver disease
-
Weight loss or loss of appetite
-
Fever
-
Chills
Early diagnosis and intervention are vital for the efficient management of liver conditions. Don’t delay seeking medical advice if you have concerns about liver-related back pain.
How is Liver Pain Diagnosed?

Diagnosing liver pain, especially when it manifests as back pain, needs a comprehensive approach to identify the underlying cause and rule out other conditions. Back pain can stem from numerous sources and so it can be misleading. Healthcare providers often start with a comprehensive medical history and physical examination while taking note of your symptoms.
Here are some common diagnostic methods used:
-
Blood tests (e.g., liver function tests that measure liver enzymes, bilirubin levels, albumin levels, and clotting factors)
-
Imaging tests
-
Ultrasound
-
Computed tomography (CT) scan
-
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
-
Liver biopsy
It’s important to note that diagnosing liver-related back pain often involves ruling out other potential causes of back pain like musculoskeletal issues, spinal conditions, and even kidney problems, which are more common. But the combination of physical findings and diagnostic test results is often helpful in accurately diagnosing the exact source of back pain and formulating effective treatment plans.
What Treatment Options Are Available for Liver-Related Back Pain?
The typical approach to treating liver-related back pain is focused on addressing the underlying condition first. This is because the back pain is often a symptom not the primary problem. The treatment plans are also highly individualized, ensuring that specific liver disease, its severity, and your overall health is dealt with.
Some of the treatment options include:
-
Antiviral medications for managing viral hepatitis (hepatitis B and C) to reduce inflammation and prevent further damage
-
Corticosteroids are often used to manage the inflammation for autoimmune hepatitis
-
Lifestyle changes are recommended for FLD like weight loss, balanced diet, and regular exercise.
-
Avoiding or stopping alcohol consumption is cornerstone for the management of alcoholic fatty liver disease
-
Diuretics are often prescribed for people with cirrhosis who are retaining extra fluid and have ascites
-
Surgical removal of tumor for early-stage cancer or any of the following
-
Chemotherapy
-
Radiation therapy
-
Targeted therapy
-
Immunotherapy
-
Liver transplant
Apart from the specific treatments for each liver condition, pain relievers are crucial aspects to alleviate the pain in the back. However, these medications should be approached cautiously and should be under medical supervision since some pain medications are harmful to an already compromised liver. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), for example, are generally avoided in patients with liver disease. It can worsen the liver’s state and may even cause bleeding.
Acetaminophen like Tylenol at reduced and controlled doses may be safer for the liver.
How Can You Prevent Liver Problems That Cause Back Pain?
The best way for you to avoid liver-related back pain is to prevent liver problems from developing. Many liver problems are linked to lifestyle choices, meaning these are modifiable and within your control. Adopting healthy habits can go a long way in protecting this important organ.
Some actionable steps you could take include:
-
Maintaining a healthy weight
-
Eating balanced nutritious food
-
Limit or avoid alcohol consumption
-
Get vaccinated
-
Avoid risky behaviors or lifestyle
-
Use medications wisely and cautiously only using when necessary
-
Manage chronic conditions (e.g., diabetes, high cholesterol, high blood pressure)
Making these proactive choices can significantly reduce your risk of developing liver problems and its associated back pain. Taking care of your liver is a long-term investment that can maintain your overall health and well-being.
Quick Summary Box
-
The intricate relationship between liver health and back pain is a connection often misunderstood
-
Liver conditions, like inflammation or more severe diseases, can manifest as pain in the back
-
Understanding the mechanisms behind the referred pain, recognizing the associated symptoms apart from the back symptoms, and knowing when to seek medical care are crucial steps in the management
-
Diagnostic processes assist health professionals pinpoint the exact cause to tailor the treatment approaches
-
Maintaining liver health through preventive measures are important in avoiding liver-related back pain
Related Resources
What is a Liver Abscess? Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
What is an Echogenic Liver? Understanding Ultrasound Findings
References
Jin, Q., Chang, Y., Lu, C., Chen, L., & Wang, Y. (2023). Referred pain: characteristics, possible mechanisms, and clinical management. Frontiers in Neurology, 14(14), 1104817. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2023.1104817
Johns Hopkins Medicine. (2025). Liver: Anatomy and Functions. Johns Hopkins Medicine. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/liver-anatomy-and-functions
Liver Cancer Pain and How Ablation Therapy Cann help. (2022, July 14). Usaoncologycenters.com. https://www.usaoncologycenters.com/sources-of-liver-cancer-pain-and-how-ablation-therapy-can-treat-it/
Liver Failure: Symptoms & Causes. (n.d.). NewYork-Presbyterian. https://www.nyp.org/digestive/liver-failure
Medications and the Liver - American College of Gastroenterology. (2011). American College of Gastroenterology. https://gi.org/topics/medications-and-the-liver/
Office of Infectious Disease and HIV/AIDS Policy (OIDP. (2016, April 20). Data and Trends. HHS.gov. https://www.hhs.gov/hepatitis/learn-about-viral-hepatitis/data-and-trends/index.html
R Bednár, D Líška, D Gurín, J Vnenčaková, A Melichová, Koller, T., & Ľ Skladaný. (2023). Low back pain in patients hospitalised with liver cirrhosis- a retrospective study. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 24(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-023-06424-8
Survival Rates» Hepatitis B Foundation. (2025). Hepb.org. https://www.hepb.org/research-and-programs/liver/staging-of-liver-cancer/survival-rates/
Zielinska, E. (n.d.). Should I Be Worried About Fatty Liver Disease? | Jefferson Health. Www.jeffersonhealth.org. https://www.jeffersonhealth.org/your-health/living-well/should-i-be-worried-about-fatty-liver-disease

Jaclyn P. Leyson-Azuela, RMT, MD, MPH, is a licensed General Practitioner and Public Health Expert. She currently serves as a physician in private practice, combining clinical care with her passion for preventive health and community wellness.



